What is lidar technology?
Lidar is an optical sensor technology that enables robots to see the world, make decisions and navigate. Robots performing simple tasks can use lidar sensors that measure space in one or two dimensions, but three dimensional (3D) lidar is useful for advanced robots designed to emulate humans. One such advanced robot is a self-driving car, where the human driver is replaced by lidar and other autonomous vehicle technologies. 3D lidar systems scan beams of light in three dimensions to create a virtual model of the environment. Reflected light signals are measured and processed by the vehicle to detect objects, identify objects, and decide how to interact with or avoid those objects.
How far can lidar technology see?
The object detection range depends on the choice of measurement process, laser, beam steering mechanism and photodetector. Short-range 3D lidars designed for low-speed vehicles in urban environments typically exhibit a range of 50 m or less. Long-range lidars designed for high-speed vehicles in highway environments can exhibit a range of 200 m or more.
What can lidar technology see?
3D lidar can determine the position, size and shape of objects. Many lidars can identify if the object is a person or cyclist, while high-resolution lidars can read text in some cases. Frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) lidar is an emerging technology trend in the autonomous vehicles market. Unlike conventional time of flight (TOF) lidar, FMCW lidar can compete with radar technology by detecting object velocity in real time. Lidars cannot see colour.
Can lidar technology see at night?
Yes, 3D lidar enables superior night vision compared to human drivers and standard cameras. Enabling safe driving in dark environments is a key motivation for car manufacturers adopting lidar technology.
Can lidar technology see in bad weather?
3D lidar performs better in poor weather compared to human drivers and standard cameras. However, poor weather performance depends on the lidar system design. For example, lidars that operate at near infrared (NIR) wavelengths are affected more by foggy conditions compared to short-wave infrared (SWIR) lidars because SWIR light is scattered less by fog than NIR light.
Can a lidar sensor get distracted by nearby lidar sensors?
It is possible, but every 3D lidar system is designed to isolate its own signals from background noise. Compared to conventional TOF lidar technology, FMCW lidar enables better signal coding to minimise the risk of interference.
Can one lidar technology emerge as the winner?
According to the market model developed by IDTechEx, this cannot happen within the next decade. The ideal 3D lidar technology depends on the type of vehicle, its level of autonomy, and its typical operating conditions.
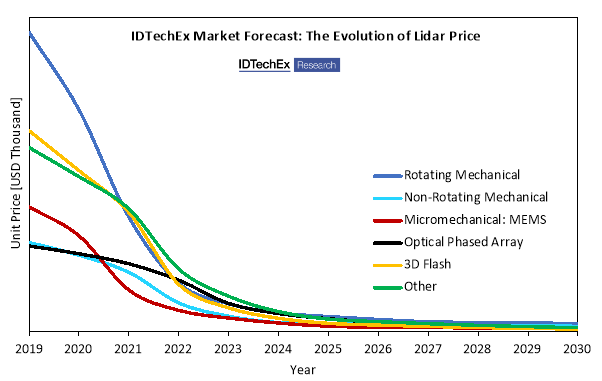
Will the price of lidar limit its adoption?
According to the market analysis by IDTechEx, the average price of a 3D lidar module in 2019 is $10,500 USD. However, unit prices will decrease rapidly within the next decade as lidar technologies mature and companies scale up production. The global market for 3D lidar in autonomous vehicles will grow to $5.4 billion by 2030.