by Tomas Zednicek Ph.D. European Passive Components Institute, EPCI Jan 19. www.passive-components.eu
1. INTRODUCTION
Tantalum capacitors are offering excellent stability in high energy, harsh conditions, and power volumetric efficiency and low parametric shift with lifetime. Are these features securing its position in new electronic designs versus its rival technologies, especially the MLCC class II capacitors and aluminium hybrid polymer capacitors?
This paper summarises recent trends in electronic industry and discuss tantalum capacitors potential in future electronic systems.
2. MARKET TRENDS
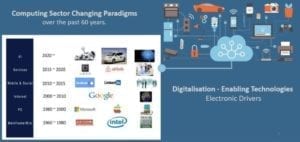
We are currently living in a fascinating time of transition into the new digital age of human history. The move is enabled by fast development of electronics and computer segment bringing completely new level of networking and services in all aspects of our lives – see Fig.1.
Fig.1. Computing sector paradigms changes and current digital services growth. Source: EPCI using Wikipedia and Depositphoto image
Completely new level of digital based services and networking are enabled by new electronic hardware, technologies with high computing, data transfer or storage capabilities. The recent platforms such as IoT, IIoT/ Industry 4.0, 5G … are calling for exponential increase of global data traffic and mobile data that the electronic hardware and infrastructure must support.
A. Major impacts to the electronic hardware requirements:
- wide increase of data to be processed on board
- move from RF to optical links (infrastructure)
- move from systems on PCB to system-on-chip
- higher density & integrated solutions
- digital, power, RF/optical signal interface to be managed within the same PCB/block, often with downsizing
- increase of dissipated power & operating temperature
- miniaturization – smaller and lower profile designs while maintaining/improving system performance
- cost & lead time reductions
B. Consequences for board design architecture changes:
- move towards wide gap semiconductor technologies (GaN/SiC) for higher speed, higher frequencies at smaller dimensions
- due to the high number of different functions and interface types, more and more different supply voltages will have to be managed separately
- multiplication of Point-of-Load and Low-Drop-Out regulator
- increase of electromagnetic compatibility constraints – protect very small digital control and data signals in increasingly noisy electrical environments
- lower voltages and higher current DC-DC converters
C. Consequences for passive components:
- low voltage, high capacitance, small size and low ESR decoupling capacitors (MLCC class II top of the interest)
- large capacitance, low voltage and low ESR bulk capacitors
- downsizing, embedding,
- thin film technology requirements
- 2D/3D printed components
- high current inductors
- overload protection by shunt resistors are mandatory
- EMI management
- introduction of 0402 RF inductors
- introduction of chip ferrite beads for power applications
references [1], [2], [3]
1. TANTALUM vs MLCC CLASS II CAPACITORS
In voltage range, tantalum capacitors have been the leader in capacitance volumetric efficiency
~ 3.3-50V for number of decades due to the combination of unique properties of Ta2O5 dielectric and high surface achieved by tantalum powder sintering technology. The unique features of Ta2O5 insulating layer includes relatively high permittivity (~27) for a stable dielectric and high electrical field strength (= relatively high breakdown voltage).
The following table summarizes the key tantalum capacitor benefit features and its value for various applications and circuit designs.
Table 1. Tantalum Capacitor Key Features and Its Importance. Source: EPCI
| Ta Capacitors Key Features | Functionality | Circuit Benefit | Applications | Limitations |
| High Stability of Electrical Parameters | Stability of parameters in harsh envorinment | Wide operating temperature; Stable performance at various working conditions (VAC,VDC, frequency) |
High Rel, Industrial, Automotive, Aerospace, Defence |
ESR, High Current Surge, Max Voltage |
|
Long Term Reliability |
Long term reliable operation |
|||
|
High Volumetric Efficiency |
High energy density in small size and low profile |
small size SMPS output filtering;
Battery Back Up |
Smartphones, SSDs,
Handhelds |
Cost |
| Battery back up; high energy
bank / local storage |
Implantable Medical /
wearable |
MLCC class II – the closest rival capacitor technology
The closest capacitor rival technology in mass volume to chip tantalum capacitors is MLCC class II capacitors based on BaTiO3 dielectric material. The material belongs to ferro-electric materials that provides very high permittivity in range of 2,000 to >30,000 that provides high capacitance in a desk type non-polar electrostatic capacitor.
Downside of the ferro-electric nature of the BaTiO3 material is its dielectric features (capacitance) sensitivity to various operating conditions such as temperature, VAC, VDC, its time stability and piezo effect. This dependence can be well used in varistors, piezo devices and other sensors, but it is an “unwanted” feature causing instability or distortion in the case of capacitors. Detail comparison of tantalum versus MLCC capacitors is not a prime focus of this article, but it can be found on EPCI web site in more details in references [4],[5],[6],[7].
The key MLCC advantage is its design flexibility and miniaturisation while keeping its cost advantages. Thus, the MLCC SMD capacitor technology has been the leader in discrete passive components miniaturisation, where 0201 case size has become the highest mass volume case size in 2018 and smaller case sizes down to 008004 are step by step adopted by consumer electronics production nowadays. MLCC technology has been also dominating the overall capacitor technologies share in both volume and value wise.
Supply Chain and Availability
MLCC capacitor market is currently going through a tough supply time period caused by multiple factors that resulted in a considerable MLCC shortage that may take another year or more to be completely resolved. During this time, attention is paid towards alternative technologies including tantalum capacitors. There are number of articles released in 2018 that address the topic of tantalum versus MLCC capacitor replacement guidelines – see [4],[5],[6].
Taking a side that qualification of a different capacitor technology on the same PCB pad position can be quite complex and complicated formal matter (despite case and performance technical compatibility), the level of possible functional replacement of tantalum to MLCC capacitors has been about 15 to 20% per feedback from customers.
Cost Matters
In a “stable” market environment, technology-based cost for 1206 case MLCC class II and A case (1206 equivalent) tantalum capacitors can be very close (depending on capacitance and voltage value). The 1206 case size is a cost down sweet-spot case size for a standard tantalum capacitor, and it can be in price competitive position to MLCC class II.
MLCC capacitors are manufactured in process sheets that are cut into individual capacitors, its cost down way (with certain limits and specific product exceptions) is downsizing. Thus, smaller case sizes 0805 and 0603 may be cheaper than 1206, even with a more expensive high tech material used. (as there are more smaller units per one process sheet produced). This is not the case of tantalum/NbO capacitors, where a standard “in-row units” manufacturing technology processing of smaller case sizes below 1206 size is more expensive.
In consequence, 0805 and 0603 tantalum capacitors may be more expensive compare to the MLCC components. However, to be fair to tantalums, it is not that easy and simple rule, as tantalums are more stable without loss of capacitance with applied voltage, thus in some cases you may end up that the stable performance tantalum cap is a cheaper solution than a MLCC solution that loses capacitance with voltage and time … lets’ discuss this more in next chapters.
0402 and 0201 tantalum case sizes are also available on the market, but are considered as some niche applications with parameters, cost and mass volume capability too far from the MLCC high volume parts to be considered for mass volume applications.
1. To ANSWER the MARKET NEEDS, TANTALUM CAPACITOR POTENTIALS
Ability of tantalum capacitors to answer the latest market trends and requirements as discussed in Chapter 2 can be assessed based on its key advantages and limitations as discussed above and summarised in Table 1.
High Volumetric Efficiency Advantage
1] Smart-phones and miniature hand-held devices
Couple of tantalum capacitors has been used in most of the mobile phones from 90’s to late 2010ish as a power supply battery back-up, filtering or audio capacitor providing high capacitance in small and low-profile case sizes.
The need for miniaturisation of the board, advances in semiconductor and circuit architectures practically eliminated the need for higher capacitance and tantalum capacitors. Position of smaller capacitance but lower ESR needed for processing power as well as coupling / decoupling has been covered by MLCC class II capacitors at the current smartphone designs.
The level of miniaturisation in mobile phones is demonstrated in Fig.2. The Nokia 3310 mobile phone was announced on 1 September 2000 being one of the most successful phones with 126 million units sold worldwide, and being one of Nokia’s most iconic devices. It used two larger and four smaller tantalum capacitors on board.
Apple iPhone X smartphone released in September 2017 inner space is occupied in ¾ by battery and only ¼ is left for the 20-layer PCB that integrates all functions. There are about 1100 MLCCs on board (no tantalum), some of them are even embedded underneath decoupling the processor – as visible in Fig.2. PCB image with removed A11 processor.
2] SSD, Enterprise SSDs, Servers
High energy, high volumetric efficiency in a low-profile design is often needed by Solid State Drives and Servers as an energy backup in case of sudden power supply interruption.
Tantalum capacitors are bringing key value with maximum volumetric efficiency above 500mJ per cc in a single component within just 1.2mm max height design. MLCC class II are excellent in miniaturisation towards small case sizes, however tantalum excels in design tasks for high energy content in larger and low profiles.
Supercapacitors could be considered as tantalum capacitors alternative in SSDs energy back up applications. It provides even higher energy density however they are lower in power density (it cannot deliver the required current fast enough within the defined case size dimensions). Tantalum capacitor manufacturers have prepared specific series [8],[9] to match with SSDs’ specific requirements and it pose an important market potential
Stable Electrical Parameters and Long-Life Time
3] Automotive
Tantalum capacitors with stable performance at wide operating temperatures, harsh environment and long term reliability has been a choice in many automotive applications under the hood, dashboard, in-cabin, entertainment, telematics etc.
The highest competition for tantalum capacitors have been aluminium electrolytic capacitors mainly due to cost down reasons. Inferior life and vibration characteristics limited their wider usage. However, with continuous advancement in aluminium capacitors, new series with higher vibration resistance or hybrid polymer types [10] that improves its reflow assembly robustness and life time stability are replacing tantalum capacitors in current designs.
Tantalum capacitors in automotive still keeps its presence mainly in the most demanding applications at continuous higher temperature operating conditions as ECUs or gearbox electronics close to the engine.
The development of V2X (vehicle to everything) supported by 5G and IoT capable hardware and networks is also needed and well utilised by automotive industry IoV (Internet of Vehicles). This has been one of the key current and future development. [16]
4] Telecom and Networking Infrastructure Hardware
Telecom base stations, switchers and other internet networking hardware has been using tantalum capacitors due to its long-life stability and reliability in various applications for DC/DC converter filtering, coupling/decoupling etc. The hardware has typical life-time of 12- 15 years that mostly excludes convention aluminium electrolytic capacitors from bulk capacitance applications.
Need for higher speed, high power in small dimension is a main driver to adopt new generation of GaN/SiC based power supplies operating at higher switching frequencies. Lower capacitance, low ESR and higher resonance frequency requirements may change output capacitor requirements towards MLCC (even class I) capacitors working together with high power inductors on the output. However, the proper set of the working point by GaN gate drive is of the key importance for overall amplifier temperature stability and linearity. Thus many new GaN boards are using tantalum capacitors for gate drive voltage stabilisation. [11]
There may be some changes in tantalum capacitor usage on board of telecom and networking hardware in near future, nevertheless there is still a need and future for this technology on board of these long life-time and long-term reliability devices.
5] Industrial Applications
Industrial applications are covering wide range of applications and requirements such as manufacturing machines, oil drilling, security, power energy generation/ transportation/ regeneration/ storage etc. The common requirements usually cover wide operating temperature, 7/24/365 operation within a low failure tolerant system.
Industrial applications may present one of most demanding operating conditions – even tighter than harsh automotive – considering that most of its life time car is in “off” state in garage, while industrial equipment has to work long-term at elevated temperature without interruption.
Tantalum capacitors are the valuable capacitor technology for industrial applications that needs continuous operation at elevated temperatures or low profile designs such as embedded controllers for industrial machines, robots etc.. as part of Industry 4.0 (IIoT) and 5.0. On the other hands tantalums are replaced by aluminium hybrid capacitors from other non-space critical, standard temperature range devices such as room temperature based solar inverters.
6] High Reliability, Aerospace, Defence and Medical Applications
High reliability market has been using tantalum capacitors for many decades and this is going to remain also in future. High energy wet and hybrid types in addition serve well some specific areas as defibrillator capacitors or 230C temperature operation inside of oil wells.
There may be some reduction in overall average selling price on the market as the trend is to use more of lower-class high reliability products or COTS+ grades.
On the other hand, the market potential such as “new space” in space applications or medical/wearables are bringing new opportunities for tantalum capacitors.
1. AROUND and BEYOND THE CURRENT TECHNOLOGY HORIZON
As mentioned, tantalum pentoxide is a material with unique dielectric properties providing stable characteristics. A next development potential aiming greater usage of tantalum capacitors has been / can be focus for example in the following areas:
- Nano-Scale storage. On-chip storage in nano-scale can be beneficial for small energy harvesting chips. Some development work announced for example by: [12]
- High Voltage High Energy Storage. Automotive EV/HEV market is in need for 400- 1000V high energy, high volumetric efficiency storage capacitors. High energy storage capacitors are also needed by power electricity regenerative energy storage fields. Current tantalum polymer capacitors extended max voltages to 125V, polymer supplier discussing potentials to increase BDV to 300V – that is not enough to tackle bigger market, but indeed a step forward. [13]
- Tantalum Thin Film Capacitors – thin and flat and/or multilayer tantalum structure based on thin film technology to answer needs for either wearable sensors or stacked designs to get lower capacitance but lower ESR design. Tantalum paste for printing of ultrathin tantalum capacitors in less than 0.2mm is available already today. [14]
- … and one day we may even print capacitors as part of 3D PCB printers. [15]
The supply chain management trend is that passive component makers are more and more concentrating on development of module solutions rather than development of individual components. This may create a next opportunity for tantalum pentoxide to support both thin film low energy and high energy power thick film passive component systems in flexible modules answering needs of wide range of applications.
2. SUMMARY and CONCLUSION
Miniaturisation, high speed data communication, processing and storage on one end and energy generation, transmission and storage on the other hand are the two main drivers for next generation of electronics.
Tantalum capacitors have been on the market for many decades recognised as the stable performance, reliable capacitor technology capable to provide high volumetric efficiency and power density.
Miniaturisation and cost down pressure allowed competing technologies to take over some portion of tantalum capacitor market:
- MLCC class II ceramic capacitor technology answers best the need for further miniaturisation and high volume production capability to support smartphones and other handhelds. There are practically no tantalum capacitors used in new designs that resulted in decrease of tantalum capacitors in mass volume
- Hybrid polymer aluminium capacitors improved robustness and stability of aluminium technology and replacing tantalum in designs where volumetric efficiency is not of a prime concern at standard operating temperature
On the other hand, new developments and future trends pose some next opportunities for tantalum capacitors to grow, specifically in the following fields:
· SSDs, enterprise SSDs, servers, embedded PCs
These applications need high energy and power density to support energy storage with constrains in dimensions / low profile.
· Telecommunication and Networking infrastructure.
Long term operation with stable electrical parameters are the value of tantalum capacitors for these low failure tolerant systems. Exponential global data and mobile data exchange with upcoming 5G standard will require continuous hardware upgrade.
· Industrial
Industry 4.0 is a next evolution step to link industrial machines by communication electronic board and processing embedded computers. Tantalum capacitors are offering its value in low profile slim design capable to operate reliable at elevated temperatures.
· High Reliability
High reliability electronics is a strong application area for tantalum capacitors with its heritage in aerospace, medical or defence applications.
Tantalum pentoxide with its unique dielectric features is presenting some more opportunities for further development that is currently under evaluation or vision as a next potential for tantalum capacitors to answer the needs of future electronic systems.
REFERENCES
- Airbus Defence and Space Roadmap for Passive Components; ESA SPCD 2018; https://passive-components.eu/airbus-defence-and-space-roadmap-for-passive-components/
- Thales Alenia Space Passive Components Roadmap 2018; ESA SPCD 2018; https://passive-components.eu/thales-alenia-space-passive-components-roadmap-2018
- Design Trends in Automotive Passives; Avnet Engineers Insight; https://passive-eu/design-trends-in-automotive-passives/
- MLCC Capacitors Availability First Aid – Tantalum/NbO to MLCC Replacement Guidelines; EPCI original article; https://passive-components.eu/mlcc-capacitors-availability- first-aid-tantalum-nbo-to-mlcc-capacitors-replacement-guidelines/
- Kemet Polymer to MLCC Shortage: When You Can’t Find The Cap You Need; https://passive-components.eu/kemet-polymer-to-mlcc-shortage-when-you-cant-find-the-cap- you-need/
- Substituting solid tantalum and tantalum polymer capacitors for SMT MLCCs; Vishay technical note; https://passive-components.eu/substituting-solid-tantalum-and-tantalum- polymer-capacitors-for-smt-mlccs/
- The Basics & Benefits of Tantalum & Ceramic Capacitors; AVX technical article; https://passive-components.eu/the-basics-benefits-of-tantalum-ceramic-capacitors/
- AVX J-Cap series http://www.avx.com/products/polymer/j-cap-series/
- Kemet T545 series http://www.kemet.com/ProductCatalog%20Documents/KEM_T2060_T545.pdf
- Panasonic Releases New Conductive Polymer Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor ZS Series; Panasonic press release; https://passive-components.eu/panasonic-releases-new- conductive-polymer-hybrid-aluminum-electrolytic-capacitor-zs-series/
- Temperature Stability Assessment of GaN Power Amplifiers with Matching Tantalum Capacitors; EPCI original article; https://passive-components.eu/epci-passive-components- tech-insight-temperature-stability-assessment-of-gan-power-amplifiers-with-matching- tantalum-capacitors/
- On a Chip Energy Storage Capacitors; 1st PCNS 2017; https://passive-eu/on-a-chip-energy-storage-capacitors/
- Pushing Tantalum capacitors to the limit: view to 300 V anodisations and beyond; HC Starck article; ESA SPCD 2018; https://passive-components.eu/pushing-tantalum-capacitors- to-the-limit-view-to-300-v-anodisations-and-beyond/
- Tantalum paste technology for the next generation of capacitors; HC Starck brochure; https://www.hcstarck-tantalum-com/products/productinformations/product_information_tantalum_paste.en.html\
- When are we going to print PCBs on 3D printer ourselves?; EPCI original article; https://passive-components.eu/when-are-we-going-to-print-pcbs-on-3d-printer-ourselves/
- Autonomous Vehicles May Not Rely on 5G; EDN original article; https://passive- components.eu/autonomous-vehicles-may-not-rely-on-5g/